As a radiology resident, you're embarking on one of the most dynamic and intellectually rewarding specialties in medicine. Diagnostic radiology combines advanced technology, precise interpretation, and direct impact on patient care. This guide builds on the foundational principles of our field—harnessing radiant energy for diagnosis and treatment while prioritizing safety—and tailors them to your training journey. Whether you're in your R1 year or preparing for boards, understanding these core elements will help you excel.
The Core of Diagnostic Radiology
Diagnostic radiology uses imaging to visualize internal structures, aiding in accurate disease diagnosis and management with minimal invasiveness.
Key modalities include:
- X-rays: Fundamental for bone and chest evaluation.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed cross-sectional views, essential for trauma and complex pathologies.
- MRI: Excels in soft tissue imaging (brain, spine, joints) without ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound: Real-time, radiation-free imaging for organs, vessels, and obstetrics.
- Fluoroscopy: Dynamic imaging for procedures like barium studies.
- Mammography: Critical for breast cancer screening.
- Bone Densitometry: Assesses osteoporosis risk.
- Interventional Radiology: Minimally invasive, image-guided therapies—a growing subspecialty.
As residents, you'll rotate through these, building proficiency in interpretation and, where applicable, performance.
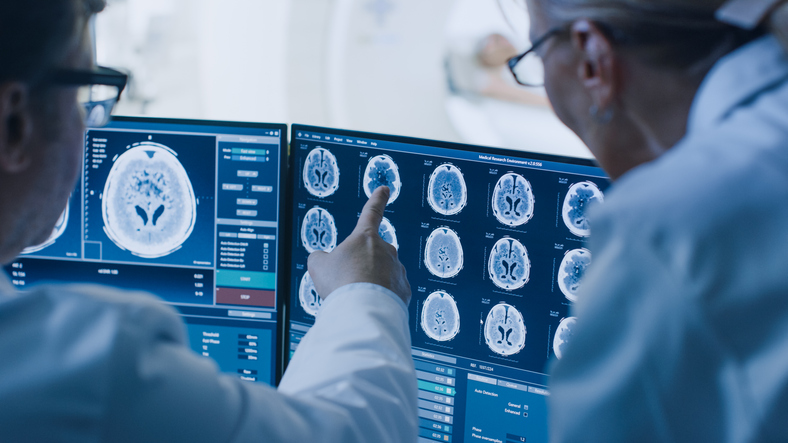
Your Training Path: The Radiology Residency Structure
Most diagnostic radiology residencies are four years long (PGY-2 to PGY-5), following a one-year preliminary internship (e.g., internal medicine, surgery, or transitional year). This structure, accredited by the ACGME, ensures comprehensive exposure.
- R1 (PGY-2): Focus on basics—plain films, CT, ultrasound, and introductory rotations in chest, abdomen, and musculoskeletal imaging.
- R2-R3: Deeper subspecialty rotations (neuroradiology, pediatrics, interventional) and procedures.
- R4: Often includes electives, mini-fellowships, or research; many attend the AIRP (American Institute for Radiologic Pathology) course.
- Call and Night Float: Builds independence in emergency imaging.
Programs emphasize gradual responsibility, with faculty supervision. Many offer pathways like ESIR (Early Specialization in Interventional Radiology) for advanced IR training.
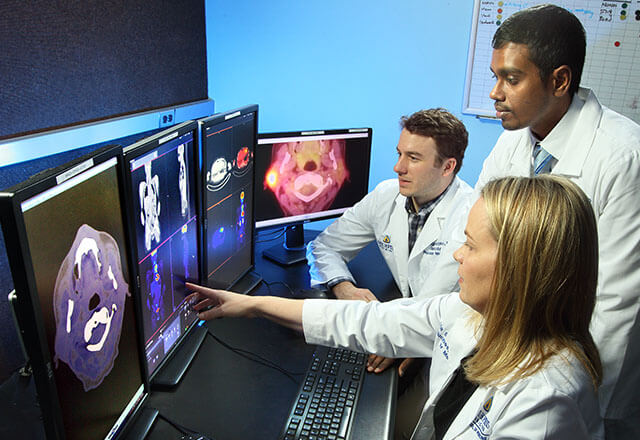
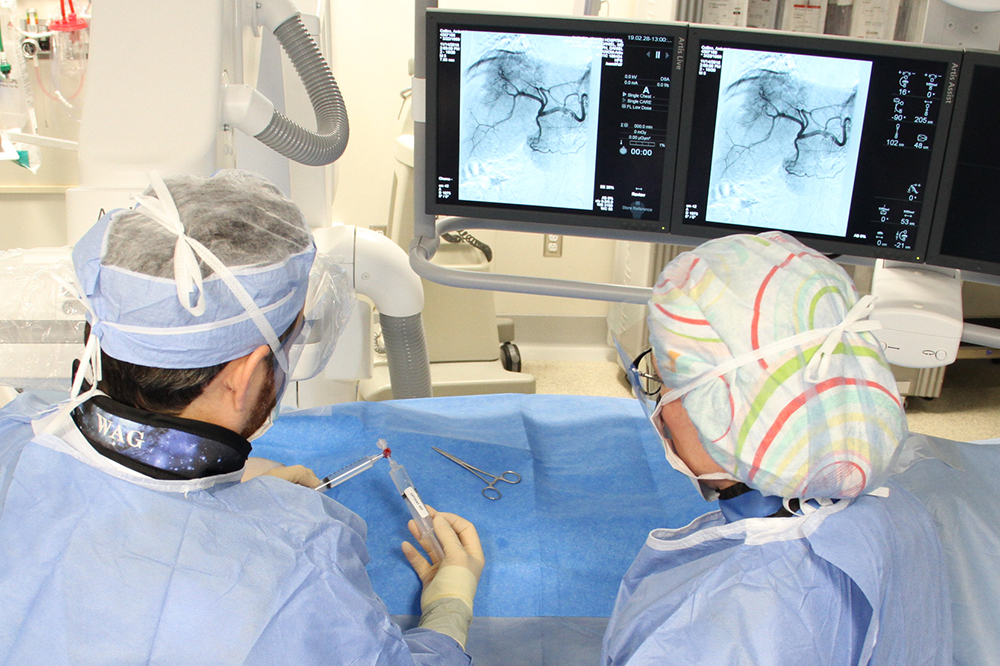
Subspecialties you'll encounter (often leading to fellowships):
- Neuroradiology
- Musculoskeletal
- Body/Abdominal
- Breast Imaging
- Cardiothoracic
- Pediatric
- Nuclear Medicine
- Interventional Radiology

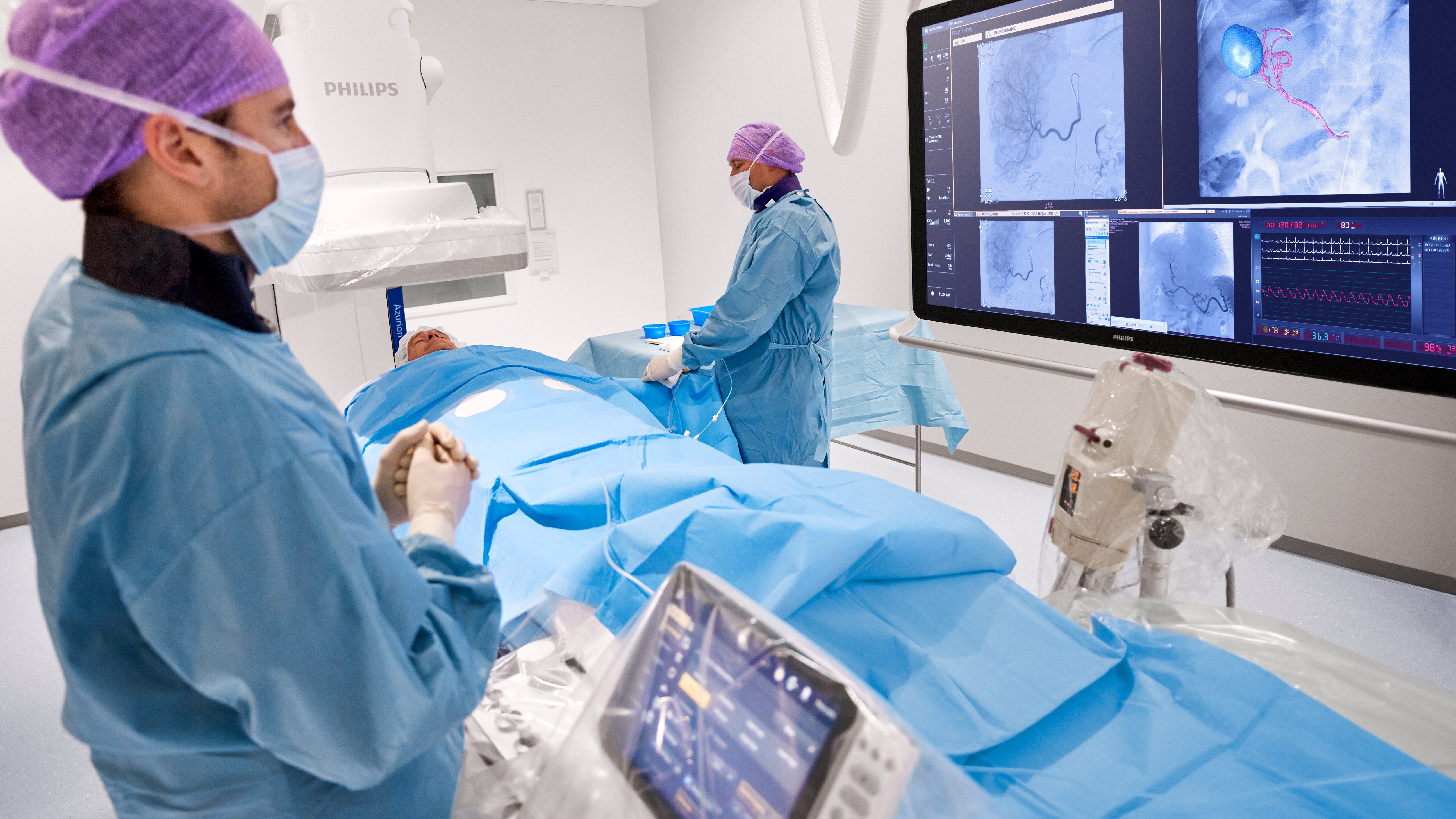
Radiation Safety: A Core Competency
Radiation protection is non-negotiable. As residents, you'll handle ionizing radiation daily, so mastering ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) is essential.
Key principles:
- Time: Minimize exposure duration.
- Distance: Double distance quarters exposure.
- Shielding: Use lead aprons, thyroid shields, and badges.
Training includes physics courses and contrast reaction management. Studies show gaps in resident knowledge, so prioritize ongoing education—formal training reduces risks for patients and staff.
Nuances: Pregnant patients/residents require special protocols; stochastic (cancer) vs. deterministic (skin burns) effects vary by dose.
Tips for Thriving in Residency
- Build Efficiency: Develop search patterns; review priors and histories.
- Study Strategically: Use core texts (e.g., Brant and Helms, ReqPrep), case files, and conferences.
- Seek Mentorship: Pair with seniors; discuss fellowship early.
- Prioritize Wellness: Burnout is real—balance call with self-care.
- Embrace Research/QI: Many programs require projects; great for CVs.
- Prepare for Boards: Core Exam after R3; Certifying Exam post-residency.
Edge cases: Night shifts test independence; medicolegal reporting in some programs hones precision.
Looking Ahead: Trends in 2026 and Beyond
Radiology evolves rapidly:
AI Integration: Tools aid detection; learn to use them ethically.Photon-Counting CT: Better resolution, lower dose.
Workforce Shifts: Teleradiology and shortages—flexibility key.
Precision Medicine: Personalized imaging protocols.
As residents, you're entering a field blending tech and humanism. Commit to lifelong learning, patient safety, and collaboration—you'll shape radiology's future.
Welcome to the reading room. You've got this!
